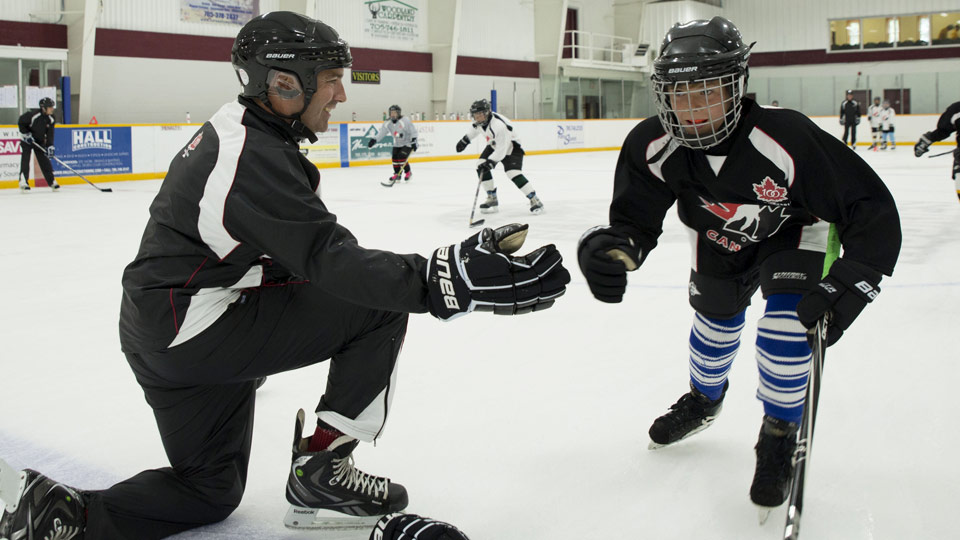
As we approach the end of July, players should be shifting their focus to preparing for the start of the new hockey season. How should players get the most development during their last few weeks of training?

When high-end players are asked how they became so good at hockey, many share stories about playing hockey all day at the municipal outdoor rink or in their backyard. You always hear about playing after school or on weekends until their parents called them home for dinner. These development paths might make sense in Minnesota or Canada, but it is hard to replicate them today in many parts of North America where outdoor rinks either don’t exist or no longer get as cold in the winter. As someone who grew up in a cold-weather climate but now lives in California, I’ve asked myself if there is a way to replicate many of the aspects of “pond hockey” development.

One of the concepts I used to shape my mindset on this topic is based on a magazine ad I saw many years ago which was endorsed by Tony Robbins. His philosophy is “How do you get the greatest result with the least amount of time or energy?” Tony refers to the ROM Quick Gym as the ‘torture machine’ – which is only a 4-minute workout but provides maximum results. So I have always tried to find ways to apply these principles to hockey with my kids since access to ice time is challenging where we live.
As a result, here are five player development activities that have had the highest return on investment (ROI) for our kids:
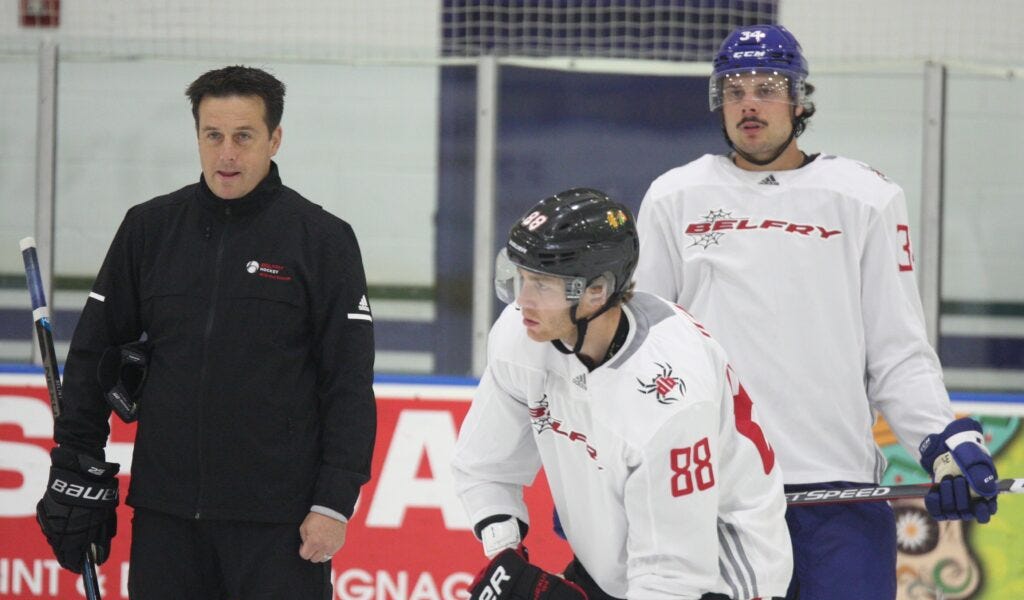

1. Hiring a Great Skills Coach
Nothing compares to a highly skilled expert teaching a player new skills. Being able to transfer insights about all the nuances of different situations combined with delivering feedback and adjustments in a productive manner can have immediate results. Unfortunately, there aren’t that many coaches who can perform at that level. Most coaches have players just running drills and giving tips that are helpful but don’t move the needle on improving a player’s in-game execution. Over the past few years, I have seen many kids of former pro players become very good hockey players. Beyond just having good genes, having someone who is an expert teach their kid the fine details of the game is certainly an advantage. Finding a coach who can provide timely, experience-based advice is invaluable.

2. Video Analysis
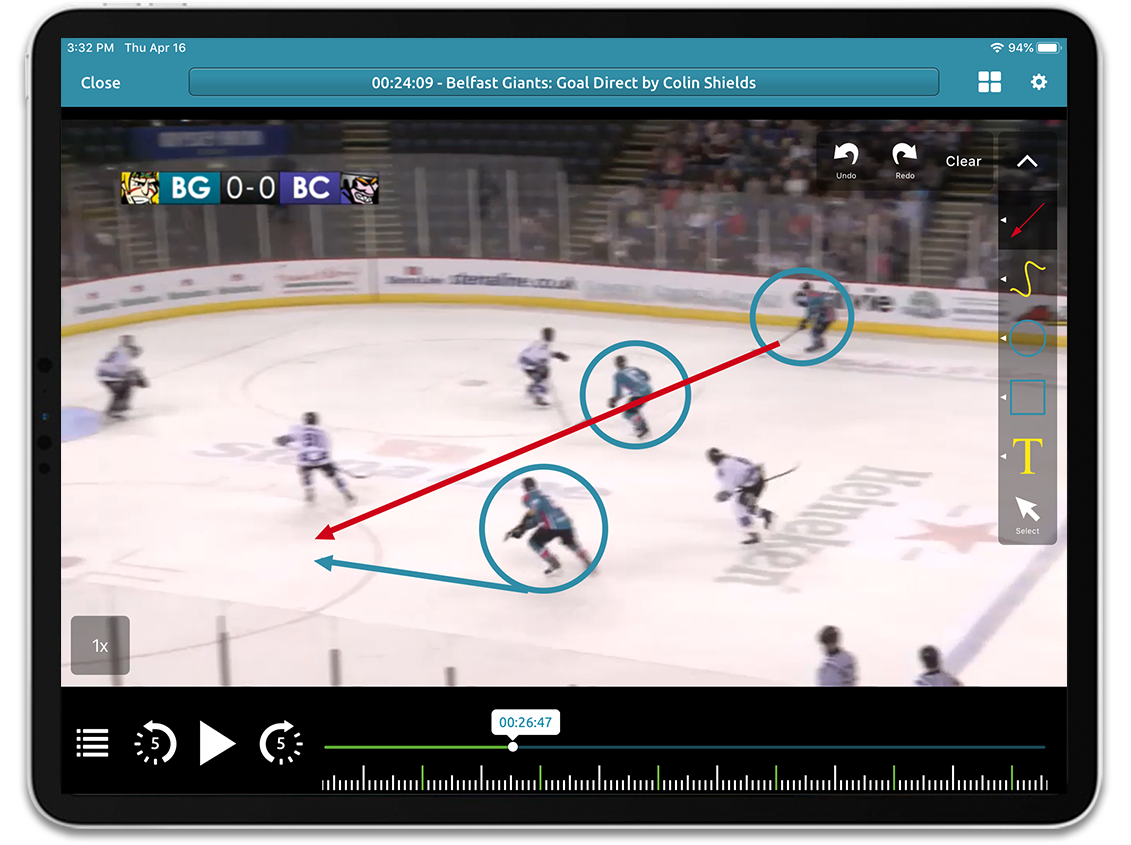
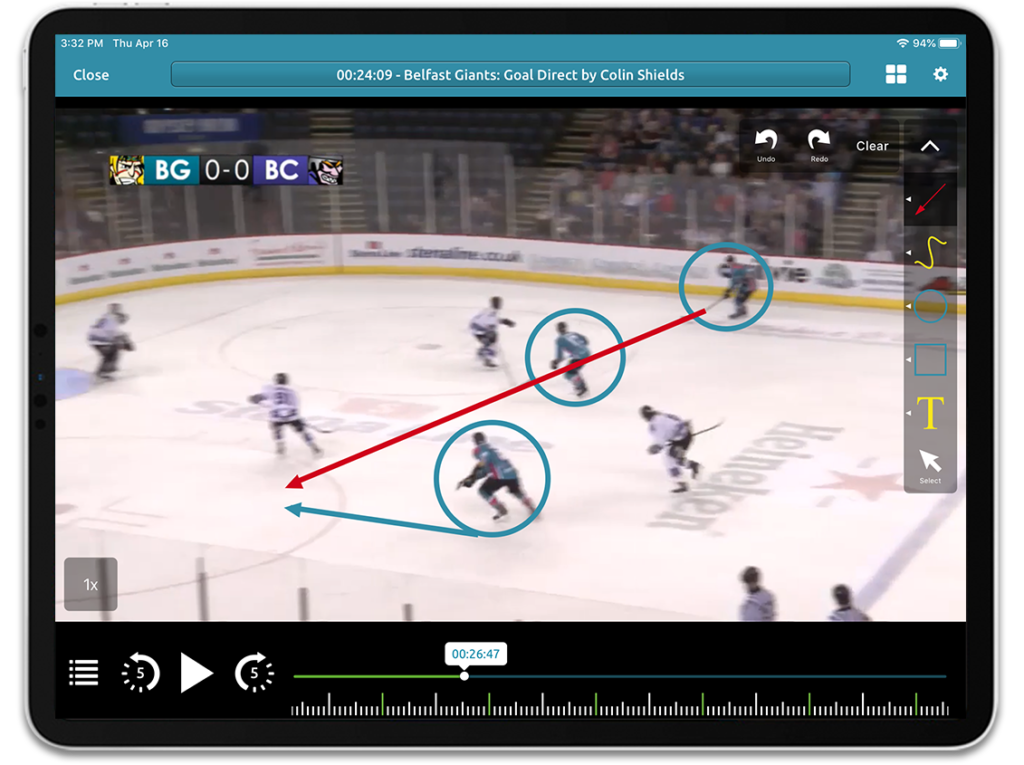
There is no better tool to learn from than watching exactly how a player performed in an actual game. Being able to analyze video footage as a way to improve is the best way for a player to see exactly how they behave in specific situations. This is why every pro and college team uses video with their players. The simplest concept to figure out how to use video is to find high-frequency, high-failure rate activities. Specifically, what does a player do most often and fail to execute? This allows a player to prioritize what to focus on in their training. Once again, this is a high ROI activity that should immediately raise the level of play for a player who can correct these failure activities.
3. Recreate Exact Game Situations When Practicing
There are many drills and practice plans that work on skills and simulate decision-making for a game. But in my experience, being able to practice executing a skill in essentially the exact conditions of a game is invaluable. Whether it is puck retrievals, stick handling in traffic, or shooting under pressure – being able to practice in nearly identical game environments is best. The hardest part of a game is to execute or make decisions under pressure and unpredictable opponents. A player who has practiced in that exact situation is more likely to execute successfully.

4. Strength and Conditioning
This is probably pretty obvious, but I am amazed at how many youth players do not take their off-ice training as seriously as their on-ice training. It is one of the few areas that a player has complete control over and a direct correlation to on-ice performance. An easy example is a player who is not in great cardio shape will be slower on the ice as a shift or game goes on. So, if you are an average-speed skater to begin with, you will appear to be below-average once fatigue sets in. Similarly, if you are easy to bump off the puck, that will show up as a turnover and spending more time chasing to get the puck back instead of being offensive. Physical training is a high ROI activity and becomes very noticeable when you don’t make that investment.

5. Skating Lessons
I have never regretted a single skating lesson my kids have taken. My kids have been lucky to work with skating instructors who work with top pro and NHL players. Every college coach will tell you how important skating is in the modern game of hockey. It is one of the first skills that a player is evaluated on. Continuing to invest in improving a player’s stride, agility, and efficiency will ensure that there will not be a ceiling on their hockey potential. Hopefully, these five different methods to get the most out of your hockey time and money investments provide some insights on where to focus. They can be somewhat obvious, but these recommendations are certainly better than “shooting 1,000 pucks in the backyard” or going to one more summer showcase when it comes to getting the best value for hockey development.
Hopefully, these five different methods to get the most out of your hockey time and money investments provide some insights on where to focus. They can be somewhat obvious, but these recommendations are certainly better than “shooting 1,000 pucks in the backyard” or going to one more summer showcase when it comes to getting the best value for hockey development.